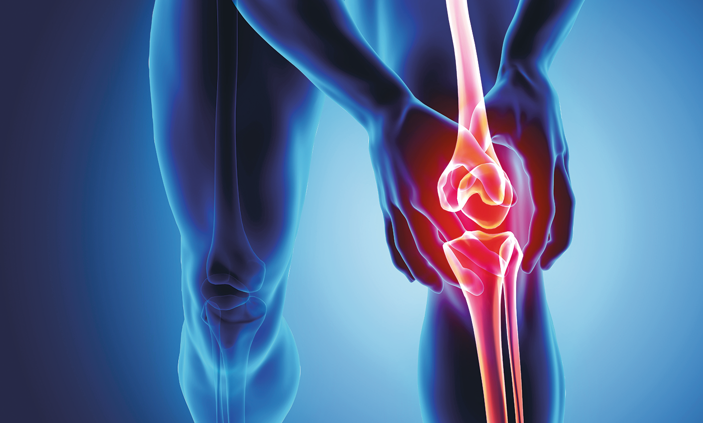
What is osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a problem that impacts the whole joint consisting of bone, cartilage material, tendons and muscle mass. Although commonly called ‘deterioration’, OA is now thought to be the result of a joint functioning extra hard to fix itself.
- Swelling of the tissue around a joint
- Damages to joint cartilage material– this is the safety cushion on the ends of your bones which enables a joint to move efficiently
- Bony spurs expanding around the edge of a joint
- Wear and tear of tendons (the hard bands that hold your joint together) and tendons (cords that connect muscles to bones)
Frequency of osteoarthritis
OA can impact any kind of joint however occurs frequently in the knees, hips, finger joints and big toe, and it can arise at any age yet tends to be more typical in people aged above 40 years or people who have had joint injuries. In particular osteoarthritis knee is becoming increasingly prominent among the elderly population in Singapore.
What can be done
Currently, there is no cure for OA. While there are therapies that can effectively regulate signs and symptoms, you should watch out for products or treatments that assert to cure OA. In order to understand this better, we turn to physiotherapists to learn more about what can be done.
Physiotherapist’s role
A physiotherapist’s role is to boost an individual’s quality of life by using a range of therapies to minimize pain and recover function or, when it comes to irreversible injury or illness, to reduce the impacts of any condition.
Physiotherapists assess, treat and take care of a wide spectrum of physical troubles. These are related to the respiratory system, cardio, neuromuscular and musculoskeletal systems of the body.
Motion and workout
Physiotherapists assess an individual’s capability to do exercise. They look at joint variety of activity, toughness, sensibility, control, balance and doing tasks.
Physical exercises raise range of motion, reinforce muscle mass and enhance balance and control. Physical exertion and exercise are effective in protecting against and managing many chronic conditions
- Workout preserves the joint’s full range of activity.
- Exercise strengthens the muscles that support the joint.
- Solid muscle mass help the joint absorb shock.
Workout doesn’t need to be tough to be useful. As a matter of fact, mild, low-impact exercises are best for knee joint inflammation. They decrease tension on the joint as they enhance its flexibility and strength. Find out more regarding osteoarthritis below.
What else you can do
Have a healthy and balanced diet plan. There is no diet regimen that will cure OA, but healthy eating and a diet targeted at preserving an ideal body mass is recommended.
Balance your life. Learn about equipment that make day-to-day tasks less complicated and how to balance recovery and activity.